
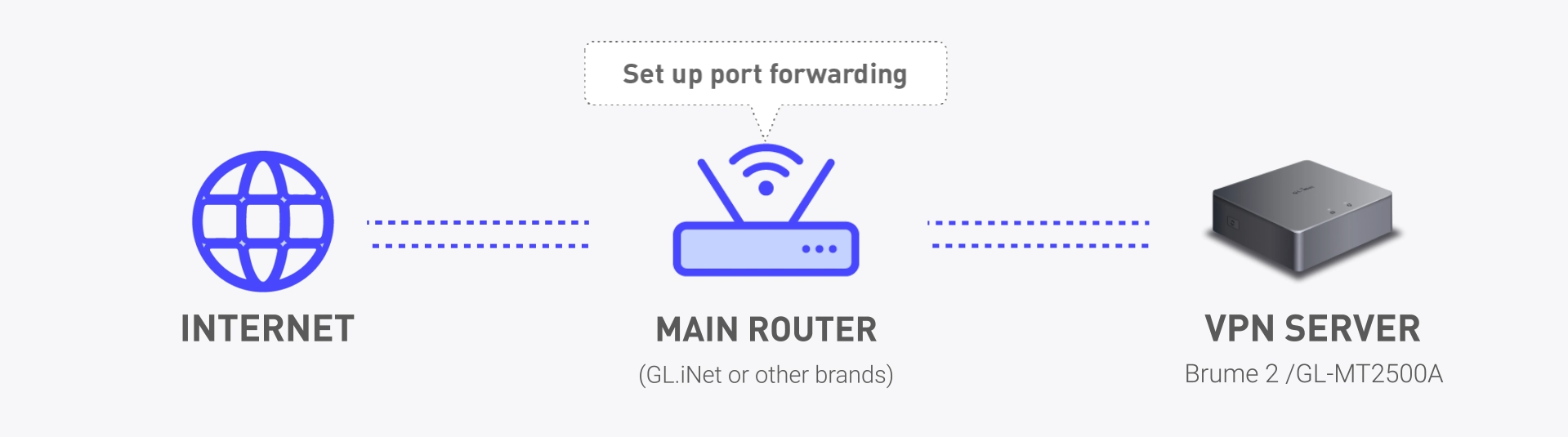
Setting up a WireGuard VPN server on a GL.iNet router allows secure (full-tunnel), remote access to your local network. If your GL.iNet router is connected to a primary router, such as an ISP router’s LAN port, you’ll need to configure port forwarding on the primary router to direct VPN traffic to your GL.iNet device. This blog article will guide you through the steps, clarify the settings, and explain key terms to make the process more clear.
When your GL.iNet router is connected to a primary router, port forwarding on the primary router is required for external traffic to reach the WireGuard server. Enable port forwarding on the main router to ensure that the external network can connect to the VPN server, specifically by opening only the port for the VPN server (ex. 51820). Once a device on the external network establishes a VPN tunnel with the GL.iNet router, the local network under the main router can be accessed through the VPN. This means not only is the GL.iNet router’s LAN accessible, but the main router’s LAN is also accessible.
1. Log in to Your Primary’s Admin Panel (or download and log in to your ISP’s mobile app):
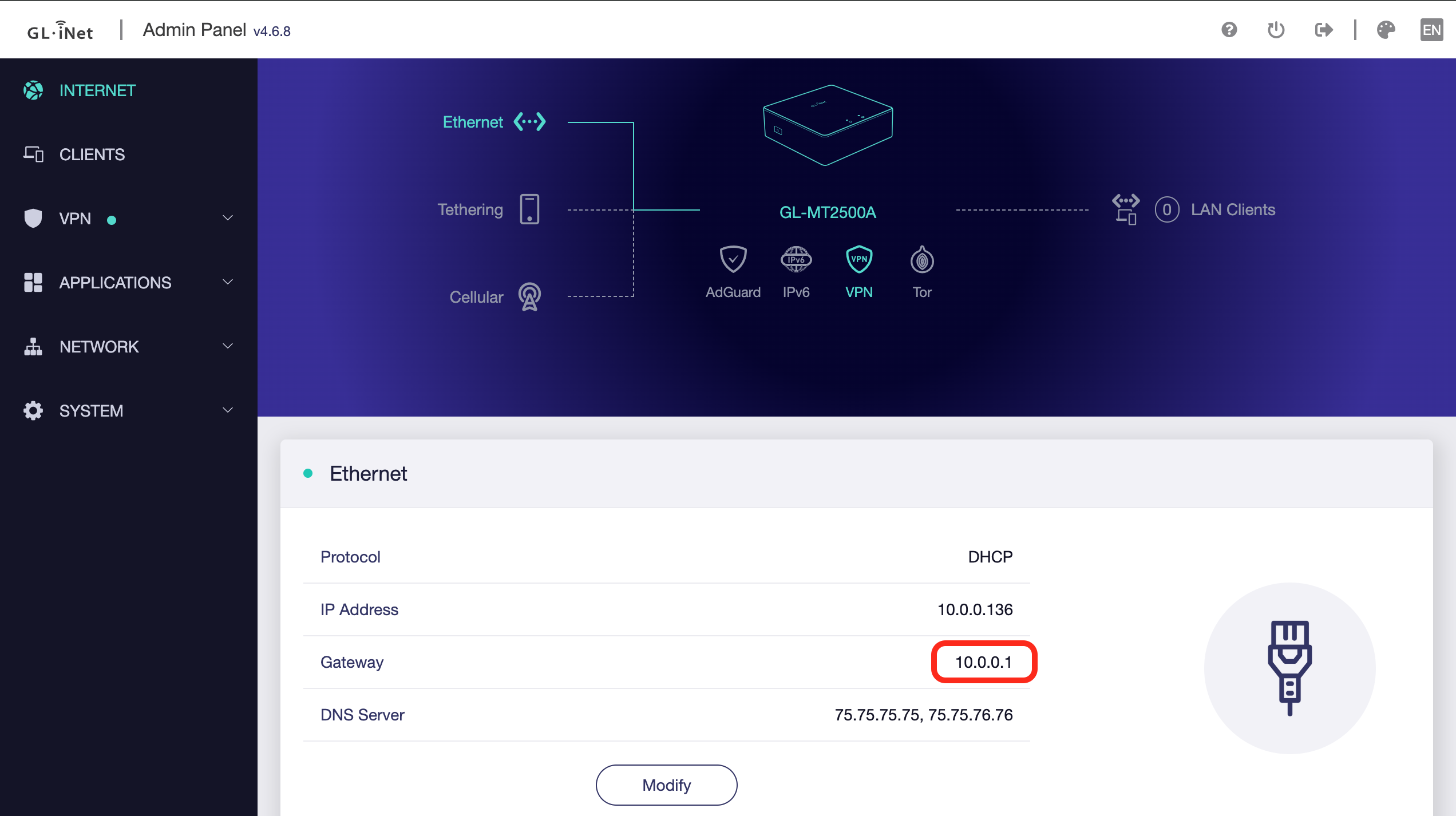
Access the admin interface by typing your primary router’s IP address into a web browser. Typically this is 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1. A quick way to determine this IP is to look at the “Gateway” IP on the Internet page of your GL.iNet router while it is connected to your home network.
2. Navigate to the Port Forwarding Section:
This section may be labeled as “Port Forwarding,” “Virtual Server,” or “NAT Forwarding,” depending on the router brand.
3. Configure the Port Forwarding Rules:
4. Set Source Port (Optional):
If your router provides a “Source Port” option, set it to “Any” (or leave it blank) to avoid restricting connections based on their originating port. WireGuard clients might use a randomized source port, especially if they’re behind NAT, and restricting this port could block legitimate connections.
5. Save and Test the Configuration:
Additional Tips
For more router-specific instructions, take a look at the GL.iNet documentation list here: https://docs.gl-inet.com/router/en/4/tutorials/how_to_set_up_port_forwarding/
Many ISPs use CGNAT to manage limited IPv4 addresses, assigning a shared public IP to multiple customers. This prevents direct access to devices and makes port forwarding impossible. If you’re behind CGNAT, consider using VPN services like Astrowarp or Tailscale, which enable secure remote access without requiring port forwarding. Click the link to check if your GL.iNet router supports Tailscale or AstroWarp. For step-by-step VPN setup instructions, refer to this video playlist.

Adam, a Virginia native with a passion for international travel, holds an Electrical Engineering degree from Virginia Tech. He is a Community Specialist at GL.iNet, creator of The Wired Nomad—a resource for digital nomads—and works full-time for the world’s largest satellite operator. Connect with him on his website.
{"one"=>"Wählen Sie 2 oder 3 Artikel zum Vergleichen aus", "other"=>"{{ count }} von 3 Elementen ausgewählt"}
Wählen Sie das erste zu vergleichende Element aus
Wählen Sie das zweite zu vergleichende Element aus
Wählen Sie das dritte Element zum Vergleichen aus